When we think of deliveries, most of us picture parcels, online shopping orders, or perhaps a pizza on a Friday night. But there’s an entirely different world of logistics happening behind the scenes — one where the temperature matters just as much as speed and where even the smallest slip-up can have serious consequences.
This is the world of the cold chain — a carefully controlled temperature journey that certain products must travel to remain safe, effective, or even alive.
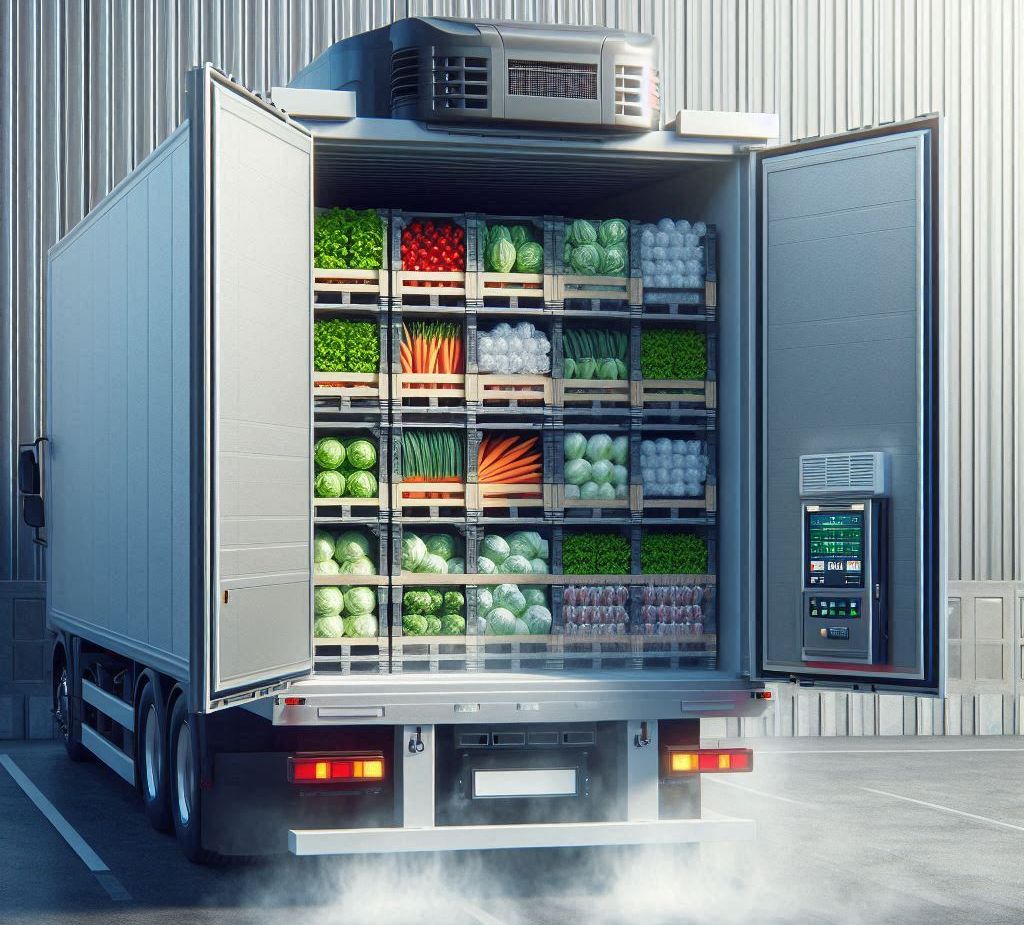

What Is the Cold Chain?
In simple terms, the cold chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain. It’s designed to transport goods that need to be kept cold (or frozen) from one place to another — often across vast distances.
Unlike regular deliveries, cold chain logistics rely on a combination of refrigeration, monitoring, and precision planning. It covers everything from storage and packaging to transport and delivery. And while the name might sound niche, the cold chain is crucial to things we use or rely on every day.
Think about vaccines, fresh produce, seafood, dairy, frozen meals, flowers, and certain medical supplies — all of these are examples of products that need to stay cold from start to finish. That’s why refrigerated couriers play such a vital role in keeping this chain intact.
Why Can’t These Items Warm Up?
For some products, warming up — even just a little — can cause irreversible damage. That’s because certain materials degrade quickly when exposed to temperatures outside of their safe range.
Take vaccines, for example. Many of them need to be kept between 2°C and 8°C. If they warm up during transit, they can lose their effectiveness — and that’s not something you can just reverse. The same goes for blood samples or organs for transplant. Even slight temperature fluctuations can make them unusable.
Food is another big one. Bacteria multiply rapidly between 5°C and 60°C, which is known as the “danger zone” in food safety. So if meat, seafood, or dairy products sit in a warm van for too long, they could become unsafe to eat — even if they still look fine.
That’s why the cold chain is built on consistency. It’s not enough to refrigerate something at the start and end of its journey. The temperature must be maintained throughout every stage — with no breaks.
How Cold Chain Deliveries Actually Work
Maintaining the cold chain isn’t just about putting things in a chilly box and hoping for the best. It’s a complex operation that relies on the right equipment, trained staff, and strict protocols.
Here’s a closer look at how it typically works:
1. Temperature-Controlled Storage
Before the product even hits the road, it’s kept in a chilled environment. This might be a cold room at a warehouse, a specialised freezer, or a climate-controlled facility depending on the product’s needs.
2. Insulated Packaging
Items are packed using materials that help keep temperatures stable — such as foam containers, gel packs, dry ice, or phase-change materials. The goal is to create a “micro-climate” that protects the item even if outside temperatures fluctuate.
3. Refrigerated Transport
The vehicles used for delivery are equipped with onboard refrigeration units that keep the cargo area within a precise temperature range. These aren’t your average vans — they often have separate temperature zones, digital controls, and backup power systems in case something goes wrong.
4. Real-Time Monitoring
Most cold chain shipments are tracked using sensors and data loggers. These devices record temperature, humidity, and sometimes even the location in real time. If the temperature starts to drift, alerts can be sent immediately so that action can be taken.
5. Last-Mile Delivery
Even the final leg of the journey — from the vehicle to the customer — is critical. Drivers are trained to handle deliveries quickly, safely, and without unnecessary delays. For some sensitive products, the package might even be handed over in a portable cooler to ensure the temperature stays consistent right to the doorstep.
Who Depends on the Cold Chain?
You might be surprised at how many industries rely on cold chain logistics. Here are just a few examples:
- Healthcare: Vaccines, insulin, blood samples, lab reagents, and organ transplants all require strict temperature control.
- Food Industry: Fresh meat, seafood, dairy, frozen meals, and even some bakery items must remain cold to stay safe and appetising.
- Floral & Agriculture: Cut flowers and certain plants wilt or die quickly if exposed to heat.
- Cosmetics & Beauty: Some high-end skincare products and organic cosmetics are temperature-sensitive.
- Laboratories & Research: Many biological samples and research materials need a stable temperature to prevent contamination or degradation.
In all these sectors, the cold chain isn’t just a convenience — it’s a necessity.
The Consequences of a Broken Cold Chain
When the cold chain fails, the results can be serious. In some cases, spoiled food leads to recalls, illness, or brand damage. In healthcare, a compromised vaccine or blood sample could risk patient safety or render months of work unusable. And in research, a broken cold chain could destroy years of irreplaceable data or materials.
That’s why businesses that depend on temperature-sensitive goods invest heavily in quality control. They partner with trusted logistics providers, conduct routine audits, and often run simulations to make sure everything works smoothly — even under stress.
Cold Chain Innovations on the Rise
As technology continues to advance, cold chain logistics is getting smarter and more efficient. Some of the latest trends include:
- Smart Sensors: Real-time tracking of temperature, location, and even light exposure — all accessible via mobile apps.
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Systems that can forecast potential cold chain failures before they happen.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Sustainable materials that still offer top-tier insulation and protection.
- Drone Delivery for Medical Supplies: In remote or hard-to-reach areas, drones are beginning to play a role in transporting urgent medical items quickly and safely.
These innovations are helping industries push the limits of what’s possible — making cold chain delivery more reliable, scalable, and environmentally friendly.
Final Thoughts
The cold chain might not be something we think about often, but it plays a silent, vital role in our daily lives. Every time you get safe food from the grocery store, every time a patient receives life-saving medication, or every time a lab gets accurate test results — the cold chain is working behind the scenes to make it all possible.
So next time you see a chilled delivery truck or an insulated package, give a little nod of appreciation. It’s not just a delivery — it’s a carefully maintained promise that the product inside is safe, fresh, and exactly as it should be.