An astronomical observatory is a dedicated facility designed for observing celestial objects and conducting space-related research. These observatories often house multiple telescopes, while some operate as single-telescope facilities. The telescopes are typically mounted in fixed positions to ensure stability and precision in observations.
Astronomical research institutions collaborate with observatories, employing scientists and experts from various countries to advance our understanding of the universe. Observatories are constructed using a variety of techniques, incorporating advanced engineering to optimize performance. Many nations contribute their expertise and technology to develop state-of-the-art telescopes, fostering international cooperation in astronomical exploration.
In Europe, there are seven prominent and operational astronomical observatories.
| Observatory Name | Location | Established | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gornergrat Observatory | Gornergrat, Switzerland | 1967 | Infrared, submillimeter |
| Sphinx Observatory | Bernese Alps, Switzerland | 1937 | Optical telescope |
| Pic du Midi Observatory | Pyrenees, France | 1878 | Optical, solar |
| Roque de los Muchachos Observatory | La Palma, Canary Islands, Spain | 1979 | Optical, infrared, solar, gamma ray |
| Teide Observatory | Tenerife, Spain | 1964 | Optical, solar, microwave |
| Calar Alto Observatory | Almeria, Spain | 1975 | Optical telescope |
| Special Astrophysical Observatory | Caucasus Mountains, Russia | 1966 | Optical telescope |
Gornergrat Observatory
There are two telescopes: one is installed in the Gornergrat Hotel, a KOSMA telescope on the southern side of the building, and an infrared telescope on the northern part.
Coordinates: 45°59′00″N 7°47′01″E
Altitude: 3,135 m (10,285 ft)
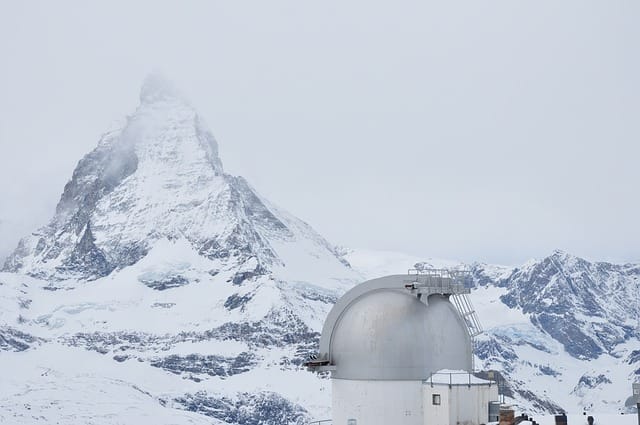

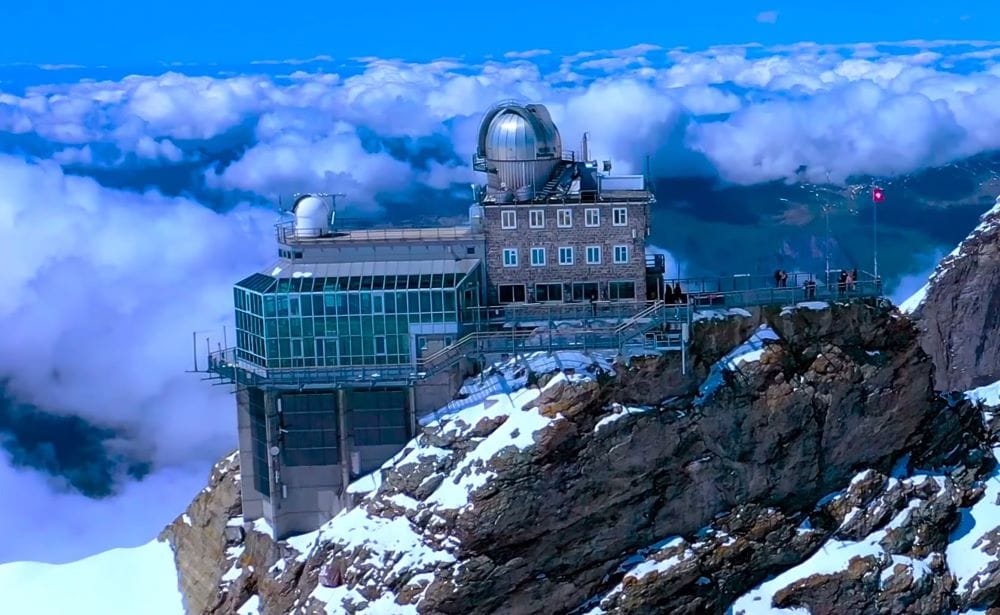
Sphinx Observatory
Located in the Swiss Alps, the Sphinx Observatory ranks as the highest-altitude observation facility in Europe and is undoubtedly a great scientific and engineering feat. This astronomical observatory was established in 1937 and is one of the most outstanding astronomical observatories in the world. Boasting a 76 cm aperture telescope, it participates in significant long-term projects related to atmospheric phenomena and astrophysical observations.
Visitors can visit the open observation deck next to the observatory, which is a panoramic view of the mountains surrounding it, including the Jungfrau region. It is not only a hub for scientific exploration but also a place of attraction for thousands of tourists annually.
Coordinates: 46°32′51″N 7°59′6″E
Altitude: 3,571 m (11,716 ft)

Pic du Midi Observatory
The Pic du Midi Observatory, as its name shows, is named after the peak Pic du Midi in France. It was established way back in the late 19th century and is only the second oldest astronomical observatory in the world, preceded only by Colombia’s National Astronomical Observatory that was established in 1878.
It is known worldwide for its contributions to research in astronomy, being a highly important site for the observation of celestial phenomena. Equipped with the finest telescopes and instruments available, it offers exceptional observation and discovery opportunities for astronomers. The high altitude of this observatory provides clear skies and little or no light pollution, making it ideal for professional and amateur astronomers. Year after year, it has helped increase our knowledge of the universe.
The Telescopes at the top:
- 0.55-metre telescope (Robley Dome)
- 0.60-metre telescope (T60 Dome)
- 1.06-metre telescope (Gentilli D)
- 2-metre telescope (Bernard Lyot Telescope)
Coordinates: 42°56′11″N 0°08′34″E
Altitude: 2,877 m (9,439 ft)

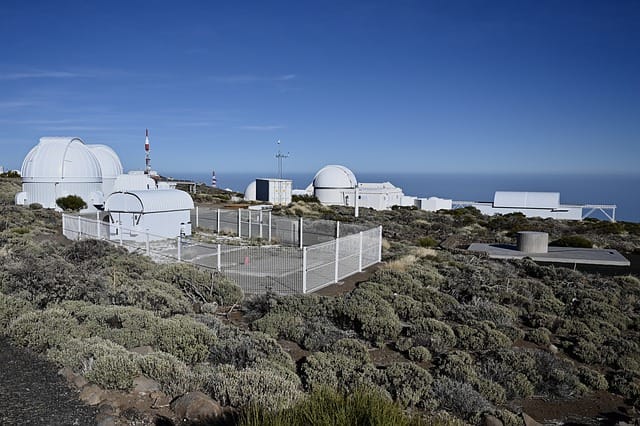
Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory
Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory, located on the Canary Island of La Palma, is a hub for astronomical research. The observatory boasts several state-of-the-art telescopes, including the Gran Telescopio Canarias, a 10.4-meter reflecting telescope that ranks among the largest single-aperture optical telescopes in the world. Also notable is the William Herschel Telescope, a 4.20-meter optical reflecting telescope that holds the title of the second-largest in Europe.
The observatory’s history dates back to 1984 when the Isaac Newton Telescope was the first to be installed on the site. Since then, the Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory has grown to become a significant center for astronomical observation and research, contributing to numerous discoveries and advancements in the field. Its strategic location and cutting-edge facilities make it an ideal site for studying the cosmos.
list of telescopes in Roque de Los Muchachos Observatory:
- Carlsberg Meridian Telescope
- Dutch Open Telescope
- Galileo National Telescope
- Gran Telescopio Canarias
- High-Energy-Gamma-Ray Astronomy
- Isaac Newton Group of Telescopes
- Isaac Newton Telescope
- Jacobus Kapteyn Telescope
- Liverpool Telescope
- Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes
- MASCARA
- Mercator Telescope
- Nordic Optical Telescope
- Swedish Solar Telescope
- SuperWASP
- William Herschel Telescope
Coordinates: 28°45′49″N 17°53′41″W
Altitude: 2,396 m (7,861 ft)

Teide Observatory
Located on the Spanish island of Tenerife, the Teide Observatory is an international facility that takes up 50 hectares and rests at an altitude of 2,390 meters above sea level. The observatory houses four solar telescopes, eight nocturnal telescopes, and four radio telescopes and thus is a very important center for both solar and astronomical observations. Between 1998 and 2002, many exoplanets were found at the Teide Observatory, which greatly increased our knowledge of planetary systems.
Observatoire: It belongs to Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), taking advantage of the remarkable atmospheric quality that Tenerife gives and that has allowed really good-quality observations throughout all of the year. Advanced spectrographs and imaging devices to continue and enhance research in this astronomical and astrophysical line will support it.
Coordinates: 28°18′00″N 16°30′35″W
Altitude: 2,390 m (7,840 ft)

Calar Alto Observatory
Calar Alto Observatory, located on the Calar Alto mountain at an elevation of 2,168 meters in Spain, is a collaborative venture built and owned by the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany and the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia in Spain. The observatory houses five reflector telescopes, with apertures of 138 inches, 87 inches, 48 inches, and 31 inches. Notably, the 138-inch reflector telescope is the largest of its kind in Europe, making it a significant asset for astronomical research.
Coordinates: 37°13′25″N 2°32′46″W
Altitude: 2,168 m (7,113 ft)

Special Astrophysical Observatory
The Russian Academy of Sciences, which is based in Russia, runs this observatory. The Radio Astronomical Telescope Academy Nauk 600 and the BTA-6 Telescope are housed in the Special Astrophysical Observatory. BTA-6 is surrounded by two tiny telescopes, manufactured by Carl Zeiss ( German scientific instrument maker from 1816–1888).
Coordinates: 43°38′49″N 41°26′26″E
Altitude: 2,070 m (6,790 ft)

Note: Several sizes of telescopes can be found inside the reserved astronomical observatory area.